
© Getty Images / iStockphoto / Freder / iStockphoto
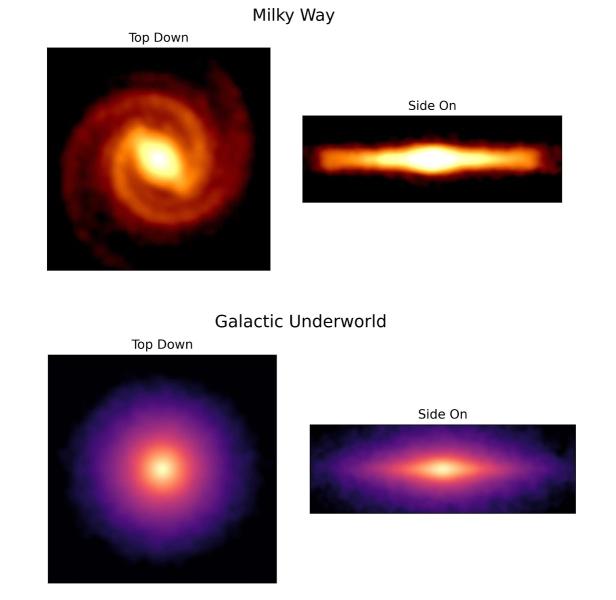
to me Milky Way About a cemetery of dead stars. This “galactic underworld,” as scientists at the University of Sydney call it, has now been mapped for the first time. Inscribed on it are the remains of billions extinguishing star.
When massive bodies die, they can do so too neutron stars or black holes will. The area in which these remains are found is approximate 3 times Like the Milky Way. “Amazing 30 percent Objects have been completely ejected from the galaxy.” David Sweeneyauthor of the study published in the journal Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society Back.
billion dead stars
To create the map, the researchers used a . file life cycle Simulated by dead stars. This enabled them to understand where their remains are now.
When massive stars die, they can range Supernova Explodes. Its core collapses, and depending on its mass, it becomes either a neutron star or a black hole. Billions of these stars have formed and died since the dawn of our galaxy. They have gone so far undetected because researchers didn’t know where to look for them.
star snooker
The main challenge was the research Speed Boost Understand that things go through a supernova. The outer shells of the stars are violently shed one by one. This can be done quickly Several million km/h is happening. Also, there is no pattern in the directions in which these eruptions occur.
“It’s a bit like snooker. If you know from what direction and at what speed the bullet hit, you can calculate where it fell. In space, objects and velocities are much greater,” Sweeney explains in the current situation.
In addition, the “table” is not flat, but dying stars go in complex orbits. There is no resistance either, which is why things never slow down their path. “Almost every remnant that has ever formed is still there, traversing through intergalactic space like ghosts,” Sweeney says.
© University of Sydney
blurred map
The resulting map of the research now shows how these objects are spread out in space. Featured spiral arms The Milky Way can no longer be seen on it. One reason for this is that supernovae blur the picture.
The side view shows that the “cemetery” reaches a level much higher than the Milky Way. Supernovae are also responsible for this. They scattered stellar debris around the visible Milky Way. Statistically, these dead stars should do just that 65 light years Fly in space far from Earth.

“Social media evangelist. Baconaholic. Devoted reader. Twitter scholar. Avid coffee trailblazer.”









More Stories
Longest jets in the universe discovered – giant particle streams as long as 140 Milky Way galaxies in a row
New method reveals 307 supernova remnants
Snapchat is upping the ante on augmented reality glasses